 Etna in Sicily erupts from 2 of its summit craters. Besides the known strombolian eruptions from the saddle vent of the New South East Crater, weak eruptions in the Northeast Crater have now been confirmed. A thermal anomaly in NE crater had been visible on sentinel satellite photos for some time. Now the mountain guide Gio Giusa climbed the crater and documented weak eruptions. They come from one of 3 small hornitos rising from the deep crater floor. Activity in the Northeast Crater was recently an indicator of a general increase in Etna’s activity. From here the activity often shifted to the central crater. This is currently quite quiet.
Etna in Sicily erupts from 2 of its summit craters. Besides the known strombolian eruptions from the saddle vent of the New South East Crater, weak eruptions in the Northeast Crater have now been confirmed. A thermal anomaly in NE crater had been visible on sentinel satellite photos for some time. Now the mountain guide Gio Giusa climbed the crater and documented weak eruptions. They come from one of 3 small hornitos rising from the deep crater floor. Activity in the Northeast Crater was recently an indicator of a general increase in Etna’s activity. From here the activity often shifted to the central crater. This is currently quite quiet.
Eruptions
News about eruptions and volcanoes can be found in this category. It is updated frequently. Volcano expert and journalist Marc Szeglat reports live from his expeditions to volcanoes.
Sangay with strong eruption
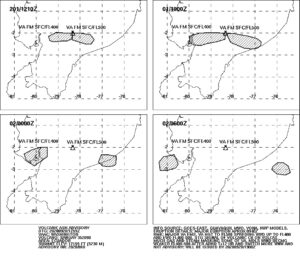 Yesterday the sangay erupted very strongly. The eruption was explosive in nature and transported volcanic ash to an altitude of 50,000 feet, which is 15,240 meters above sea level. The VAAC reported the ash cloud at 12:59 UCT. In Ecuador it was 7:59 a.m. More explosions followed during the day, in which the explosions lost some of their force but still carried ash at more than 10,000 meters above sea level. At different altitudes, the air currents blew in different directions: The lower part of the eruption cloud was transported westward, the upper part eastward. This circumstance caused ash rain in 6 of the 24 provinces of the country. The regional airport of Guayaquil temporarily stopped its operations because the ash endangered air traffic. The country’s government promised to help the cattle ranchers to remove the ashes. It covers the pastures and contaminates the drinking water, not only for the cattle.
Yesterday the sangay erupted very strongly. The eruption was explosive in nature and transported volcanic ash to an altitude of 50,000 feet, which is 15,240 meters above sea level. The VAAC reported the ash cloud at 12:59 UCT. In Ecuador it was 7:59 a.m. More explosions followed during the day, in which the explosions lost some of their force but still carried ash at more than 10,000 meters above sea level. At different altitudes, the air currents blew in different directions: The lower part of the eruption cloud was transported westward, the upper part eastward. This circumstance caused ash rain in 6 of the 24 provinces of the country. The regional airport of Guayaquil temporarily stopped its operations because the ash endangered air traffic. The country’s government promised to help the cattle ranchers to remove the ashes. It covers the pastures and contaminates the drinking water, not only for the cattle.
Sangay with further volcanic eruptions
 The Ecuadorian volcano Sangay keeps the local press busy, as it continues to be active and once ventured out of its cloud cover. On pictures you can see that on the southern flank of the volcano a deep channel has been created, through which lava flows and pyroclastic flows flow. In addition, the sangay is explosively active and promotes volcanic ash. The VAAC registered it today at an altitude of 6000 m. The ash drifts in a westerly direction. Media reports say that ash clouds have risen up to 870 m above crater height. Lahars now pose a permanent threat and influence the hydrology of the river landscape at the foot of the mighty volcano. Sangay is located at the edge of the Amazon basin, in one of the wettest regions on earth.
The Ecuadorian volcano Sangay keeps the local press busy, as it continues to be active and once ventured out of its cloud cover. On pictures you can see that on the southern flank of the volcano a deep channel has been created, through which lava flows and pyroclastic flows flow. In addition, the sangay is explosively active and promotes volcanic ash. The VAAC registered it today at an altitude of 6000 m. The ash drifts in a westerly direction. Media reports say that ash clouds have risen up to 870 m above crater height. Lahars now pose a permanent threat and influence the hydrology of the river landscape at the foot of the mighty volcano. Sangay is located at the edge of the Amazon basin, in one of the wettest regions on earth.
Pacaya erupts lava flows on 17.09.20
 The Guatemalan volcano Pacaya is still active today and erupts at least one lava flow, which flows over the southern flank of the volcano and has a length of 400 m. MIROVA registers a high thermal radiation with 234 MW power, which confirms the lava flow. The photo should show this lava flow. The exact date of the photo is not known. On the screenshot you can see not only the lava flowing out of a tunnel in the lower part of the McKenney cone, but also the volcanoes Agua and Fuego in the background. Speaking of McKenney crater. This one erupts strombolian. According to reports from INSIVUMEH, the ejection height of glowing tephra is up to 100 m.
The Guatemalan volcano Pacaya is still active today and erupts at least one lava flow, which flows over the southern flank of the volcano and has a length of 400 m. MIROVA registers a high thermal radiation with 234 MW power, which confirms the lava flow. The photo should show this lava flow. The exact date of the photo is not known. On the screenshot you can see not only the lava flowing out of a tunnel in the lower part of the McKenney cone, but also the volcanoes Agua and Fuego in the background. Speaking of McKenney crater. This one erupts strombolian. According to reports from INSIVUMEH, the ejection height of glowing tephra is up to 100 m.
Fuego with double strike
 The Fuego in Guatemela never gets tired of spewing lava. Yesterday a rare double impact was recorded when 2 strombolian eruptions occurred directly after each other. Glowing tephra was ejected several hundred meters high. The lumps landed on the volcano flank and went down as debris avalanches.
The Fuego in Guatemela never gets tired of spewing lava. Yesterday a rare double impact was recorded when 2 strombolian eruptions occurred directly after each other. Glowing tephra was ejected several hundred meters high. The lumps landed on the volcano flank and went down as debris avalanches.
INSIVUMEH reports 8-11 explosive eruptions per hour. The tephra rises up to 300 m above crater level. Volcanic ash makes it to 4700 m above sea level. The volcano continues to be effusive and erupts a lava flow. It flows through the erosion gully of Ceniza and is a good 100 m long. The warning of lahars remains because of the heavy rainfall. For the same reason our LiveCam has failed again. Despite water-protected technology it always finds a way to paralyze the cam. Ulli is trying to get the camera back online as soon as possible.
Fuego increases activity in September
 The Fuego in Guatemala has further increased its effusive and explosive activity. INSIVUMEH reports an increase in activity that began on September 5. However, there are significant variations in the intensity of activity. For example, a lava flow flows in the channel of Cenzia, whose length fluctuates between 100 and 650 m. On a recent sentinel satellite photo in the infrared range, the lava flow can be clearly seen. Hot avalanches are ejected from the lava front. Additionally, explosive eruptions occur. The VAAC Darwin issued 2 Vona warnings today, after which volcanic ash was detected at an altitude of 4600 m. Glowing tephra is ejected several hundred meters high and triggers debris avalanches on the flank. On the seismograms one can see numerous vibrations. Sometimes the explosions generate seismic signals with large peak amplitudes. Unfortunately, it is precisely during this phase of increased activity that our LiveCam failed. Our man on site is trying to get it back online quickly.
The Fuego in Guatemala has further increased its effusive and explosive activity. INSIVUMEH reports an increase in activity that began on September 5. However, there are significant variations in the intensity of activity. For example, a lava flow flows in the channel of Cenzia, whose length fluctuates between 100 and 650 m. On a recent sentinel satellite photo in the infrared range, the lava flow can be clearly seen. Hot avalanches are ejected from the lava front. Additionally, explosive eruptions occur. The VAAC Darwin issued 2 Vona warnings today, after which volcanic ash was detected at an altitude of 4600 m. Glowing tephra is ejected several hundred meters high and triggers debris avalanches on the flank. On the seismograms one can see numerous vibrations. Sometimes the explosions generate seismic signals with large peak amplitudes. Unfortunately, it is precisely during this phase of increased activity that our LiveCam failed. Our man on site is trying to get it back online quickly.Irazu: Antennas collapsed
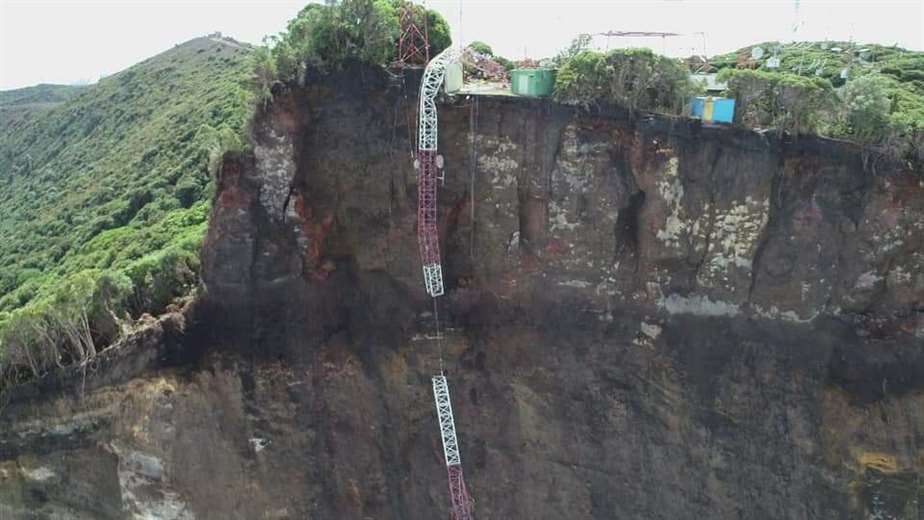
Yesterday at the Costa Rican volcano Irazu, 2 telecommunication antennas and a building collapsed and fell into the abyss near the crater. The abyss had been created by a colossal landslide in the summit area of the volcano in late August. Before that, crevasses had formed and there were hundreds of ground tremors.
The Volcanological and Seismological Observatory of Costa Rica (Ovsicori) reported that during an overflight it was discovered that the building and two antennas had collapsed towards the cliff. Whether there was another landslide is not clear from the report. But what you can see very nicely on the photos is the sheer size of the landslide in the volcano flank.
Fuego erupts 2 lava flows
 The Guatemalan volcano Fuego again increased its activity and erupted explosively and effusively. INSIVUMEH registers between 11 and 15 explosions per hour. Some of the explosions have a high acoustic pressure and produce clear peaks on the seismogram. Ear witnesses report loud explosion noises that can still be heard in the villages at the foot of the volcano. Volcanic ash rises to an altitude of 4700 m and drifts up to 15 km in an easterly direction. Glowing tephra is ejected and descends on the flanks. There it produces hot debris avalanches. They are in competition with 2 short lava flows: the longer one flows through the gorge La Trinidad and has travelled about 250 meters. The shorter lava flow reaches 100 m and travels through the Cenzia Gorge.
The Guatemalan volcano Fuego again increased its activity and erupted explosively and effusively. INSIVUMEH registers between 11 and 15 explosions per hour. Some of the explosions have a high acoustic pressure and produce clear peaks on the seismogram. Ear witnesses report loud explosion noises that can still be heard in the villages at the foot of the volcano. Volcanic ash rises to an altitude of 4700 m and drifts up to 15 km in an easterly direction. Glowing tephra is ejected and descends on the flanks. There it produces hot debris avalanches. They are in competition with 2 short lava flows: the longer one flows through the gorge La Trinidad and has travelled about 250 meters. The shorter lava flow reaches 100 m and travels through the Cenzia Gorge.
Etna glows
 Etna in Sicily continues its weak activity. An Italian volcano observer shared in the social media a picture taken from Linguaglossa in the northeast of the volcano. The picture shows red illuminated steam rising from 2 craters. The craters are the Northeast Crater and the New South East Crater. Both vents show thermal anomalies on satellite images. Probably there are also deep seated strombolian eruptions in the New Southeast Crater. However, these are currently so small that the tephra does not rise above the crater rim. But that is not enough: A sentinel image from Sunday also reveals a thermal anomaly in Bocca Nuova. It is even the most distinctive of the 3 anomalies. So it could be that the central crater could soon play a central role in the eruption process again.
Etna in Sicily continues its weak activity. An Italian volcano observer shared in the social media a picture taken from Linguaglossa in the northeast of the volcano. The picture shows red illuminated steam rising from 2 craters. The craters are the Northeast Crater and the New South East Crater. Both vents show thermal anomalies on satellite images. Probably there are also deep seated strombolian eruptions in the New Southeast Crater. However, these are currently so small that the tephra does not rise above the crater rim. But that is not enough: A sentinel image from Sunday also reveals a thermal anomaly in Bocca Nuova. It is even the most distinctive of the 3 anomalies. So it could be that the central crater could soon play a central role in the eruption process again.
The tremor moves sideways in the yellow area and fluctuates occasionally. The quake activity has decreased in the last 3 days and can be considered moderate.
Copahue erupts volcanic ash
 The Chilean volcano Copahue erupted an ash cloud yesterday, which rose to an altitude of 3700 m and drifted in a southeasterly direction. Already last week there was a comparable ash emission
The Chilean volcano Copahue erupted an ash cloud yesterday, which rose to an altitude of 3700 m and drifted in a southeasterly direction. Already last week there was a comparable ash emission
Copahue is located in the Bio Bio region and on the border with Argentina. The complex stratovolcano consists mainly of andesite. El Agrio is currently active from about a dozen craters. An acidic crater lake is bubbling in this crater. The Copahue is covered by a glacier. Larger volcanic eruptions threaten lahars. The alarm status is “yellow”.
